Work With Multi-Band Rasters
Last updated on 2023-01-03 | Edit this page
WARNING
Warning in
download.file("http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/physical/ne_110m_graticules_all.zip", :
cannot open URL
'https://www.naturalearthdata.com/http/www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/physical/ne_110m_graticules_all.zip':
HTTP status was '404 Not Found'ERROR
Error in download.file("http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/physical/ne_110m_graticules_all.zip", : cannot open URL 'http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/110m/physical/ne_110m_graticules_all.zip'Overview
Questions
- How can I visualize individual and multiple bands in a raster object?
Objectives
- Identify a single vs. a multi-band raster file.
- Import multi-band rasters into R using the
rasterpackage. - Plot multi-band color image rasters in R using the
ggplotpackage.
Things You’ll Need To Complete This Episode
See the lesson homepage for detailed information about the software, data, and other prerequisites you will need to work through the examples in this episode.
We introduced multi-band raster data in an earlier lesson. This episode explores how to import and plot a multi-band raster in R.
Getting Started with Multi-Band Data in R
In this episode, the multi-band data that we are working with is imagery collected using the NEON Airborne Observation Platform high resolution camera over the NEON Harvard Forest field site. Each RGB image is a 3-band raster. The same steps would apply to working with a multi-spectral image with 4 or more bands - like Landsat imagery.
If we read a RasterStack object into R using the
raster() function, it only reads in the first band.
R
RGB_band1_HARV <- raster("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif")
We need to convert this data to a data frame in order to plot it with
ggplot.
R
RGB_band1_HARV_df <- as.data.frame(RGB_band1_HARV, xy = TRUE)
R
ggplot() +
geom_raster(data = RGB_band1_HARV_df,
aes(x = x, y = y, alpha = layer)) +
coord_quickmap()

R
RGB_band1_HARV
OUTPUT
class : RasterLayer
band : 1 (of 3 bands)
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141 (nrow, ncol, ncell)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
source : HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
names : layer
values : 0, 255 (min, max)Notice that when we look at the attributes of this band, we see:
band: 1 (of 3 bands)
This is R telling us that this particular raster object has more bands (3) associated with it.
Image Raster Data Values
As we saw in the previous exercise, this raster contains values between 0 and 255. These values represent degrees of brightness associated with the image band. In the case of a RGB image (red, green and blue), band 1 is the red band. When we plot the red band, larger numbers (towards 255) represent pixels with more red in them (a strong red reflection). Smaller numbers (towards 0) represent pixels with less red in them (less red was reflected). To plot an RGB image, we mix red + green + blue values into one single color to create a full color image - similar to the color image a digital camera creates.
Import A Specific Band
We can use the raster() function to import specific
bands in our raster object by specifying which band we want with
band = N (N represents the band number we want to work
with). To import the green band, we would use band = 2.
R
RGB_band2_HARV <- raster("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif", band = 2)
We can convert this data to a data frame and plot the same way we plotted the red band:
R
RGB_band2_HARV_df <- as.data.frame(RGB_band2_HARV, xy = TRUE)
R
ggplot() +
geom_raster(data = RGB_band2_HARV_df,
aes(x = x, y = y, alpha = layer)) +
coord_equal()

We’d expect a brighter value for the forest in band 2 (green) than in band 1 (red) because the leaves on trees of most often appear “green” - healthy leaves reflect MORE green light than red light.
Raster Stacks in R
Next, we will work with all three image bands (red, green and blue) as an R RasterStack object. We will then plot a 3-band composite, or full color, image.
To bring in all bands of a multi-band raster, we use
thestack() function.
R
RGB_stack_HARV <- stack("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif")
Let’s preview the attributes of our stack object:
R
RGB_stack_HARV
OUTPUT
class : RasterStack
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141, 3 (nrow, ncol, ncell, nlayers)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
names : HARV_RGB_Ortho_1, HARV_RGB_Ortho_2, HARV_RGB_Ortho_3
min values : 0, 0, 0
max values : 255, 255, 255 We can view the attributes of each band in the stack in a single output:
R
RGB_stack_HARV@layers
OUTPUT
[[1]]
class : RasterLayer
band : 1 (of 3 bands)
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141 (nrow, ncol, ncell)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
source : HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
names : HARV_RGB_Ortho_1
values : 0, 255 (min, max)
[[2]]
class : RasterLayer
band : 2 (of 3 bands)
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141 (nrow, ncol, ncell)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
source : HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
names : HARV_RGB_Ortho_2
values : 0, 255 (min, max)
[[3]]
class : RasterLayer
band : 3 (of 3 bands)
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141 (nrow, ncol, ncell)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
source : HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
names : HARV_RGB_Ortho_3
values : 0, 255 (min, max)If we have hundreds of bands, we can specify which band we’d like to view attributes for using an index value:
R
RGB_stack_HARV[[2]]
OUTPUT
class : RasterLayer
band : 2 (of 3 bands)
dimensions : 2317, 3073, 7120141 (nrow, ncol, ncell)
resolution : 0.25, 0.25 (x, y)
extent : 731998.5, 732766.8, 4712956, 4713536 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
crs : +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
source : HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
names : HARV_RGB_Ortho_2
values : 0, 255 (min, max)We can also use the ggplot functions to plot the data in
any layer of our RasterStack object. Remember, we need to convert to a
data frame first.
R
RGB_stack_HARV_df <- as.data.frame(RGB_stack_HARV, xy = TRUE)
Each band in our RasterStack gets its own column in the data frame. Thus we have:
R
str(RGB_stack_HARV_df)
OUTPUT
'data.frame': 7120141 obs. of 5 variables:
$ x : num 731999 731999 731999 731999 732000 ...
$ y : num 4713535 4713535 4713535 4713535 4713535 ...
$ HARV_RGB_Ortho_1: num 0 2 6 0 16 0 0 6 1 5 ...
$ HARV_RGB_Ortho_2: num 1 0 9 0 5 0 4 2 1 0 ...
$ HARV_RGB_Ortho_3: num 0 10 1 0 17 0 4 0 0 7 ...Let’s create a histogram of the first band:
R
ggplot() +
geom_histogram(data = RGB_stack_HARV_df, aes(HARV_RGB_Ortho_1))
OUTPUT
`stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.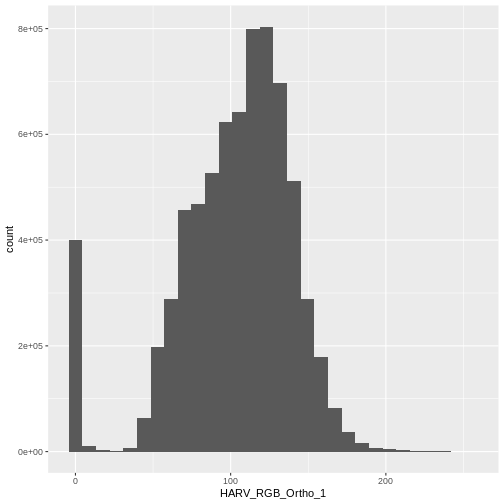
And a raster plot of the second band:
R
ggplot() +
geom_raster(data = RGB_stack_HARV_df,
aes(x = x, y = y, alpha = HARV_RGB_Ortho_2)) +
coord_quickmap()

We can access any individual band in the same way.
Create A Three Band Image
To render a final three band, colored image in R, we use the
plotRGB() function.
This function allows us to:
- Identify what bands we want to render in the red, green and blue
regions. The
plotRGB()function defaults to a 1=red, 2=green, and 3=blue band order. However, you can define what bands you’d like to plot manually. Manual definition of bands is useful if you have, for example a near-infrared band and want to create a color infrared image. - Adjust the
stretchof the image to increase or decrease contrast.
Let’s plot our 3-band image. Note that we can use the
plotRGB() function directly with our RasterStack object (we
don’t need a dataframe as this function isn’t part of the
ggplot2 package).
R
plotRGB(RGB_stack_HARV,
r = 1, g = 2, b = 3)
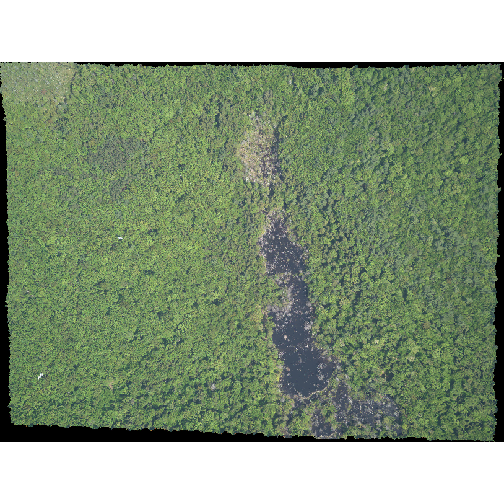

The image above looks pretty good. We can explore whether applying a
stretch to the image might improve clarity and contrast using
stretch="lin" or stretch="hist".
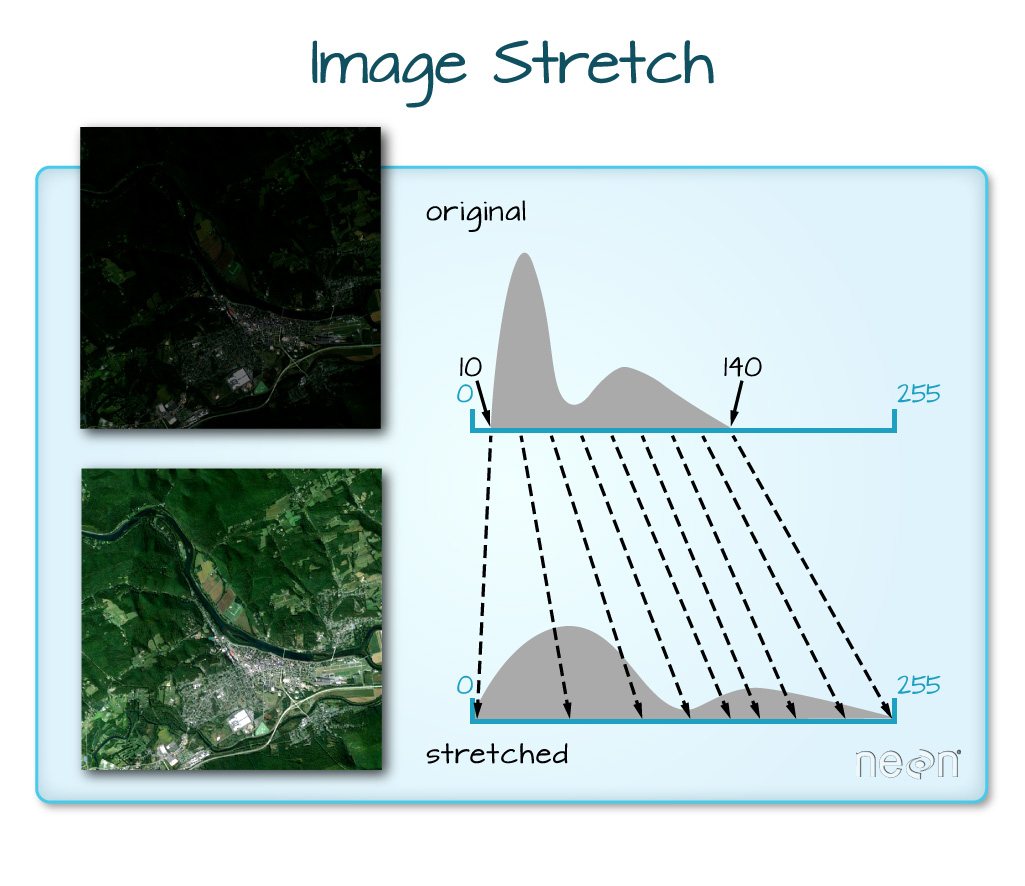
When the range of pixel brightness values is closer to 0, a darker image is rendered by default. We can stretch the values to extend to the full 0-255 range of potential values to increase the visual contrast of the image.
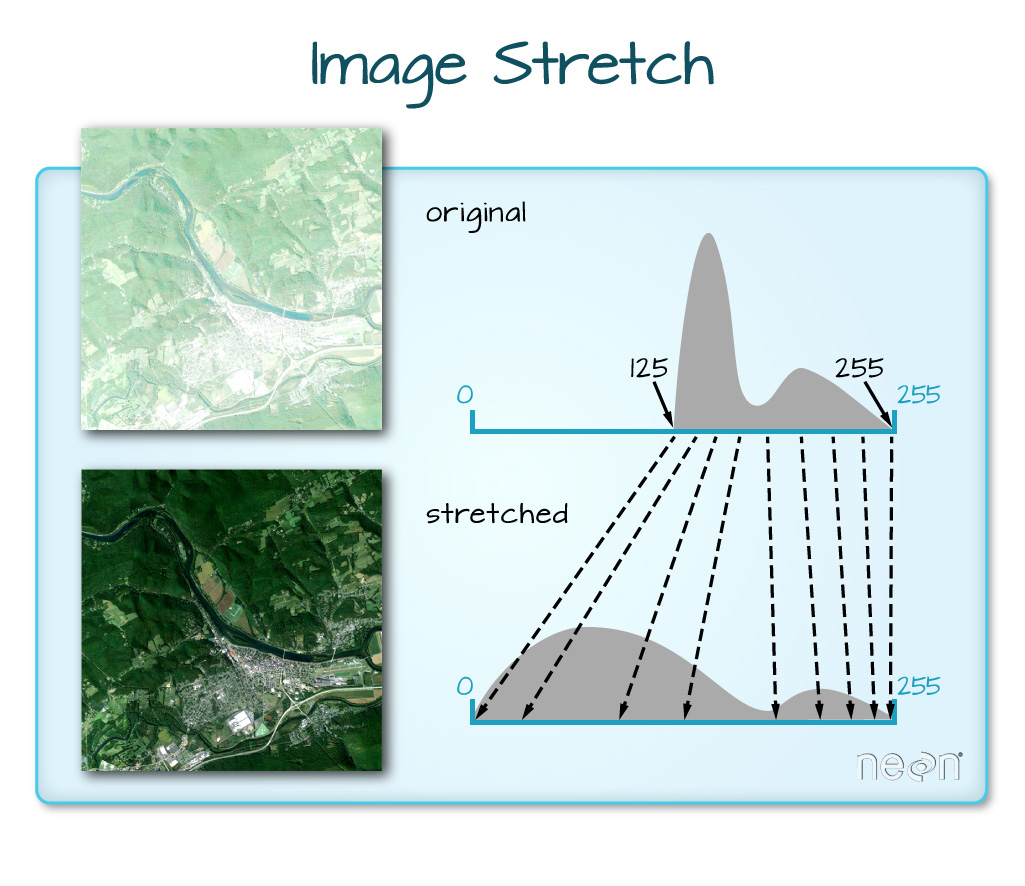
When the range of pixel brightness values is closer to 255, a lighter image is rendered by default. We can stretch the values to extend to the full 0-255 range of potential values to increase the visual contrast of the image.
R
plotRGB(RGB_stack_HARV,
r = 1, g = 2, b = 3,
scale = 800,
stretch = "lin")
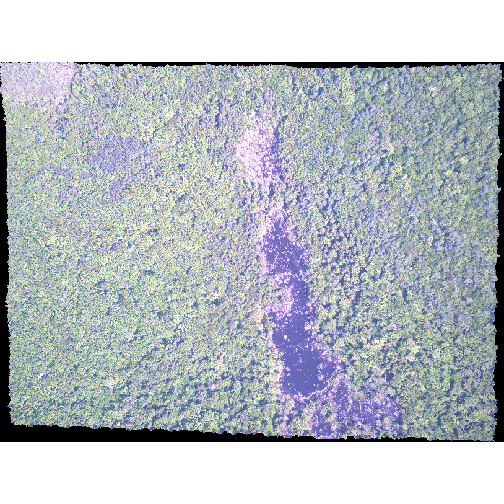

R
plotRGB(RGB_stack_HARV,
r = 1, g = 2, b = 3,
scale = 800,
stretch = "hist")
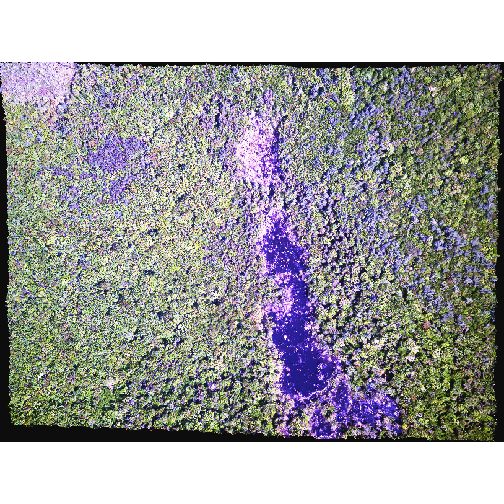

In this case, the stretch doesn’t enhance the contrast our image significantly given the distribution of reflectance (or brightness) values is distributed well between 0 and 255.
Challenge - NoData Values
Let’s explore what happens with NoData values when working with
RasterStack objects and using the plotRGB() function. We
will use the HARV_Ortho_wNA.tif GeoTIFF file in the
NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARVRGB_Imagery/
directory.
- View the files attributes. Are there
NoDatavalues assigned for this file? - If so, what is the
NoDataValue? - How many bands does it have?
- Load the multi-band raster file into R.
- Plot the object as a true color image.
- What happened to the black edges in the data?
- What does this tell us about the difference in the data structure
between
HARV_Ortho_wNA.tifandHARV_RGB_Ortho.tif(R objectRGB_stack). How can you check?
- First we use the
GDALinfo()function to view the data attributes.
R
GDALinfo("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_Ortho_wNA.tif")
WARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersWARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersWARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersOUTPUT
rows 2317
columns 3073
bands 3
lower left origin.x 731998.5
lower left origin.y 4712956
res.x 0.25
res.y 0.25
ysign -1
oblique.x 0
oblique.y 0
driver GTiff
projection +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
file data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_Ortho_wNA.tif
apparent band summary:
GDType hasNoDataValue NoDataValue blockSize1 blockSize2
1 Float64 TRUE -9999 1 3073
2 Float64 TRUE -9999 1 3073
3 Float64 TRUE -9999 1 3073
apparent band statistics:
Bmin Bmax Bmean Bsd
1 0 255 107.83651 30.01918
2 0 255 130.09595 32.00168
3 0 255 95.75979 16.57704
Metadata:
AREA_OR_POINT=Area From the output above, we see that there are
NoDatavalues and they are assigned the value of -9999.The data has three bands.
To read in the file, we will use the
stack()function:
R
HARV_NA <- stack("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_Ortho_wNA.tif")
- We can plot the data with the
plotRGB()function:
R
plotRGB(HARV_NA,
r = 1, g = 2, b = 3)
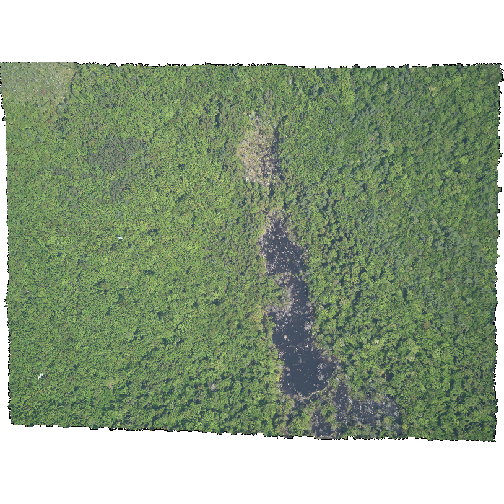

- The black edges are not plotted.
- Both data sets have
NoDatavalues, however, in the RGB_stack the NoData value is not defined in the tiff tags, thus R renders them as black as the reflectance values are 0. The black edges in the other file are defined as -9999 and R renders them as NA.
R
GDALinfo("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif")
WARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersWARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersWARNING
Warning: GDAL support is provided by the sf and terra packages among othersOUTPUT
rows 2317
columns 3073
bands 3
lower left origin.x 731998.5
lower left origin.y 4712956
res.x 0.25
res.y 0.25
ysign -1
oblique.x 0
oblique.y 0
driver GTiff
projection +proj=utm +zone=18 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs
file data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/RGB_Imagery/HARV_RGB_Ortho.tif
apparent band summary:
GDType hasNoDataValue NoDataValue blockSize1 blockSize2
1 Float64 TRUE -1.7e+308 1 3073
2 Float64 TRUE -1.7e+308 1 3073
3 Float64 TRUE -1.7e+308 1 3073
apparent band statistics:
Bmin Bmax Bmean Bsd
1 0 255 NaN NaN
2 0 255 NaN NaN
3 0 255 NaN NaN
Metadata:
AREA_OR_POINT=Area Data Tip
We can create a RasterStack from several, individual single-band GeoTIFFs too. We will do this in a later episode, Raster Time Series Data in R.
RasterStack vs RasterBrick in R
The R RasterStack and RasterBrick object types can both store multiple bands. However, how they store each band is different. The bands in a RasterStack are stored as links to raster data that is located somewhere on our computer. A RasterBrick contains all of the objects stored within the actual R object. In most cases, we can work with a RasterBrick in the same way we might work with a RasterStack. However a RasterBrick is often more efficient and faster to process - which is important when working with larger files.
We can turn a RasterStack into a RasterBrick in R by using
brick(StackName). Let’s use the object.size()
function to compare RasterStack and RasterBrick objects. First we will
check the size of our RasterStack object:
R
object.size(RGB_stack_HARV)
OUTPUT
51688 bytesNow we will create a RasterBrick object from our RasterStack data and view its size:
R
RGB_brick_HARV <- brick(RGB_stack_HARV)
object.size(RGB_brick_HARV)
OUTPUT
170898632 bytesNotice that in the RasterBrick, all of the bands are stored within the actual object. Thus, the RasterBrick object size is much larger than the RasterStack object.
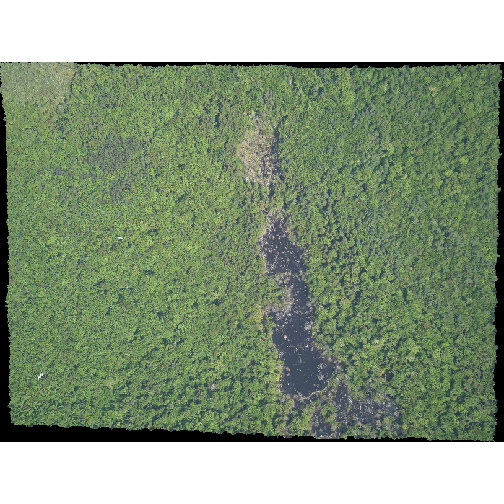
You use the plotRGB() function to plot a RasterBrick
too:
R
plotRGB(RGB_brick_HARV)

Challenge: What Functions Can Be Used on an R Object of a particular class?
We can view various functions (or methods) available to use on an R
object with methods(class=class(objectNameHere)). Use this
to figure out:
- What methods can be used on the
RGB_stack_HARVobject? - What methods can be used on a single band within
RGB_stack_HARV? - Why do you think there is a difference?
- We can see a list of all of the methods available for our RasterStack object:
R
methods(class=class(RGB_stack_HARV))
OUTPUT
[1] ! != [
[4] [[ [[<- [<-
[7] %in% == $
[10] $<- addLayer adjacent
[13] aggregate all.equal animate
[16] approxNA area Arith
[19] as.array as.character as.data.frame
[22] as.integer as.list as.logical
[25] as.matrix as.vector atan2
[28] bbox blockSize boxplot
[31] brick calc cellFromRowCol
[34] cellFromRowColCombine cellFromXY cellStats
[37] clamp click coerce
[40] colFromCell colFromX colSums
[43] Compare coordinates corLocal
[46] couldBeLonLat cover crop
[49] crosstab crs<- cut
[52] cv density dim
[55] dim<- disaggregate dropLayer
[58] extend extent extract
[61] flip freq getValues
[64] getValuesBlock getValuesFocal hasValues
[67] head hist image
[70] init inMemory interpolate
[73] intersect is.factor is.finite
[76] is.infinite is.na is.nan
[79] isLonLat KML labels
[82] length levels levels<-
[85] log Logic mask
[88] match Math Math2
[91] maxValue mean merge
[94] metadata minValue modal
[97] mosaic names names<-
[100] ncell ncol ncol<-
[103] nlayers nrow nrow<-
[106] origin origin<- overlay
[109] pairs persp plot
[112] plotRGB predict print
[115] proj4string proj4string<- quantile
[118] raster rasterize ratify
[121] readAll readStart readStop
[124] reclassify rectify res
[127] res<- resample rotate
[130] rowColFromCell rowFromCell rowFromY
[133] rowSums sampleRandom sampleRegular
[136] scale select setMinMax
[139] setValues shift show
[142] spplot stack stackSelect
[145] stretch subs subset
[148] Summary summary t
[151] tail text trim
[154] unique unstack values
[157] values<- weighted.mean which.max
[160] which.min whiches.max whiches.min
[163] wkt writeRaster xFromCell
[166] xFromCol xmax xmax<-
[169] xmin xmin<- xres
[172] xyFromCell yFromCell yFromRow
[175] ymax ymax<- ymin
[178] ymin<- yres zonal
[181] zoom
see '?methods' for accessing help and source code- And compare that with the methods available for a single band:
R
methods(class=class(RGB_stack_HARV[1]))
WARNING
Warning in .S3methods(generic.function, class, envir): 'class' is of length > 1;
only the first element will be usedOUTPUT
[1] [ [<- anyDuplicated as_tibble as.data.frame
[6] as.raster bind boxplot brick cellFromXY
[11] coerce coordinates determinant distance duplicated
[16] edit extent extract head initialize
[21] isSymmetric Math Math2 Ops raster
[26] rasterize relist subset summary surfaceArea
[31] tail trim unique values<- weighted.mean
[36] writeValues
see '?methods' for accessing help and source code- There are far more things one could or want to ask of a full stack than of a single band.
