Summary and Schedule
ATTENTION This is an experimental test of The Carpentries Workbench lesson infrastructure. It was automatically converted from the source lesson via the lesson transition script.
If anything seems off, please contact Zhian Kamvar zkamvar@carpentries.org
FIXME: Add information about fMRI analysis in Neuroimaging
{% comment %} This is a comment in Liquid {% endcomment %}
Prerequisites
Attendees must have some base familiarity with Python in order to comfortably progress through the lesson
| Setup Instructions | Download files required for the lesson | |
| Duration: 00h 00m | 1. Course Overview and Introduction |
What steps do I need to take before beginning to work with fMRI
data? Learn about fMRIPrep derivatives |
| Duration: 00h 25m | 2. Exploring Preprocessed fMRI Data from fMRIPREP |
How does fMRIPrep store preprocessed neuroimaging data How do I access preprocessed neuroimaging data |
| Duration: 00h 50m | 3. Introduction to Image Manipulation using Nilearn | How can be perform arithmetic operations on MR images |
| Duration: 01h 35m | 4. Integrating Functional Data |
How is fMRI data represented How can we access fMRI data along spatial and temporal dimensions How can we integrate fMRI and structural MRI together |
| Duration: 02h 20m | 5. Cleaning Confounders in your Data with Nilearn | How can we clean the data so that it more closely reflects BOLD instead of artifacts |
| Duration: 02h 50m | 6. Applying Parcellations to Resting State Data |
How can we reduce amount of noise-related variance in our data? How can we frame our data as a set of meaningful features? |
| Duration: 03h 30m | 7. Functional Connectivity Analysis | How can we estimate brain functional connectivity patterns from resting state data? |
| Duration: 04h 30m | Finish |
The actual schedule may vary slightly depending on the topics and exercises chosen by the instructor.
Setting up the tutorial environment
Binder
Using Binder is the easiest and fastest way to get started with the workshop. Binder is a virtual environment containing the full computing environment required in order to go through the workshop. Note that Binder hosts the environment on a cloud server and therefore internet access is required to launch it.
Setting up Binder
Step 1:
Click the link here to spin up the workshop environment: Binder Workshop You will see an interface that looks like the following:
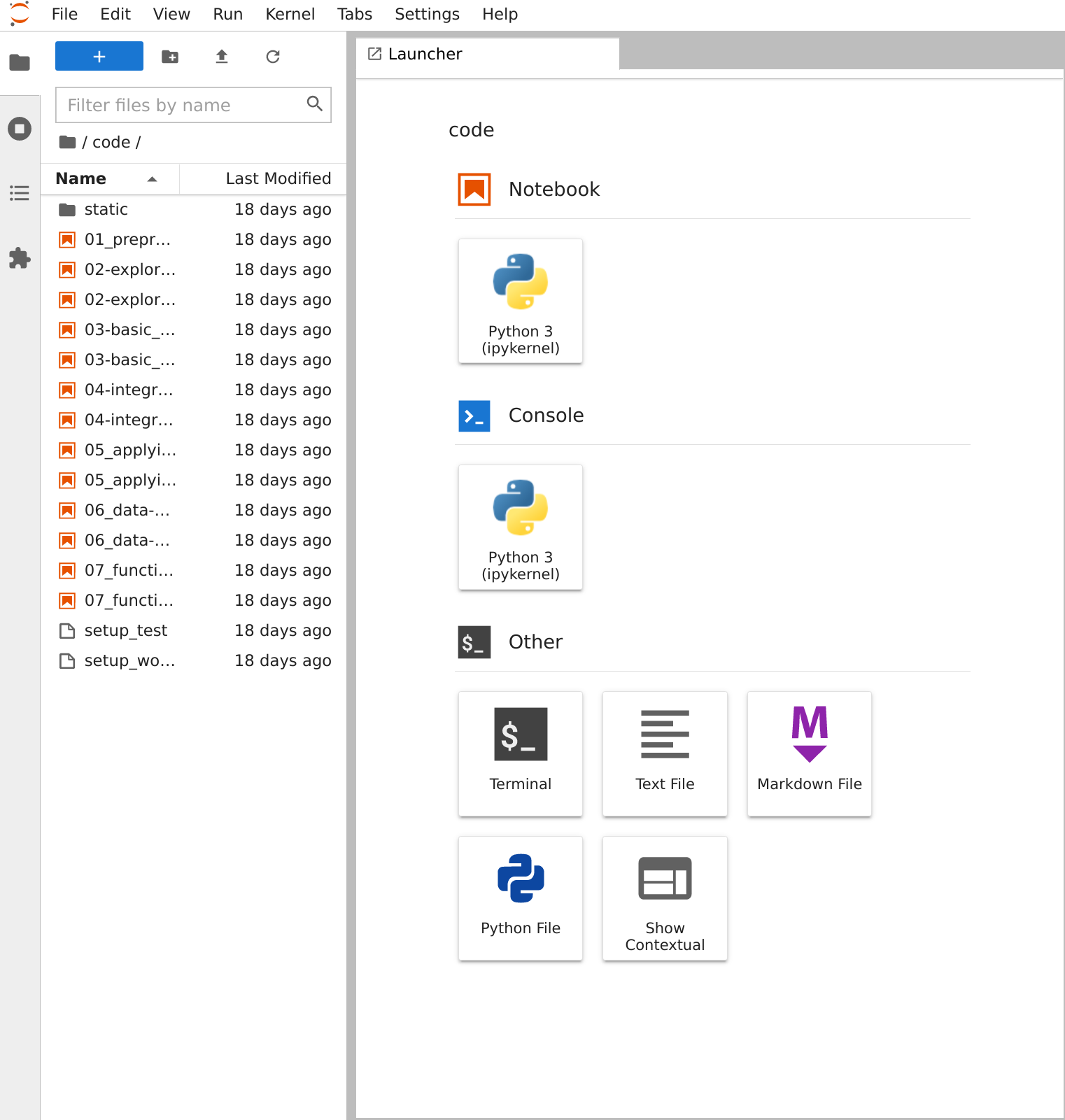
The left-hand pane shows a list of workshop notebooks that contain the content of the workshop itself. Before jumping into the workshop notebooks we need to perform a setup step to pull the neuroimaging data that will be used in the workshop…
Run the setup_workshop script
./setup_workshop
Hit enter once pasted and you should see the following
{alt='Console Filled' class="img-static"}
This will begin downloading the data required for the workshop onto your Binder instance so that it is usable for the workshop. Once started *do not close the tab by pressing the "x" button.* Instead, you may now open and begin working through the workshop notebooks.
## Getting workshop material locally
### Method 1: Downloading directly from the repository
On the GitHub repo (this page), click the green button that says "Clone or download", then click **Download ZIP**. Once downloaded, extract the ZIP file.
### Method 2: Using Git
Using this method requires a (very) useful piece of software called <code>git</code>. The process of installing git depends heavily on whether you're using MacOS, Windows or Linux. Follow the instructions in the link below to set up <code>git</code> on your PC:
[Installing Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git)
Once you've installed <code>git</code>, open up your terminal and do the following:
git clone https://github.com/carpentries-incubator/SDC-BIDS-fMRI.git
This will download the repository directly into your current directory.
### Setting up Python environment
We use python version 3.6.0, but any newer version should also work (Python 2 versions haven't been tested). There are many methods to setting up a python environment but we'd recommend using some sort of virtual environment as to not break your system python install. Two methods (of many) are listed below:
### Method 1: Setting up conda environment (easiest) [Windows, Linux, MacOS]
For easy set-up we recommend [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/download/) to manage python packages for scientific computing. Once installed, setting up the python environment can be done quite easily:
#### Windows
1. Install Anaconda Python version 3.7
2. Open **Anaconda Navigator**
3. Click on **Environments** on the left pane
4. Click **Create** then type in <code>sdc-bids-fmri</code>
5. In the <code>sdc-bids-fmri</code> entry click the play button then click **Open Terminal**
6. In terminal type:
conda install -y numpy pandas scipy scikit-learn matplotlib jupyter ipykernel nb_conda conda install -y -c conda-forge awscli pip install nilearn nibabel
7. Close the terminal, click on the play button again and open **Jupyter Notebook**
8. Navigate to <code>sdc-bids-fmri</code> folder you downloaded earlier.
9. Done!
#### [Linux](Linux) and MacOS
After installing Anaconda, open terminal and type:
cd sdc-bids-fmri conda create -p ./sdc-fmri source activate $(pwd)/sdc-fmri conda install numpy pandas scipy scikit-learn matplotlib jupyter ipykernel nb_conda conda install -c conda-forge awscli pip install nilearn nibabel
##### Method 2: Using pyenv [Linux, MacOS]
An alternative method uses [pyenv](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv) with [pyenv virtualenv](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv). This is a favourite because it seamlessly integrates multiple python versions and environments into your system while maintaining use of pip (instead of conda).
cd sdc-bids-fmri pyenv virtualenv 3.6.0 sdc-fmri echo sdc-fmri > .python-version pip install –requirement requirements.txt
## Acquiring the data
This tutorial uses data derived from the **UCLA Consortium for Neuropsychiatric Phenomics LA5c Study [1]**.
To download (**warning: large download size!**) the subset of the data used for the tutorial:
cd sdc-bids-fmri
download T1w scans
cat download_list |
xargs -I ‘{}’ aws s3 sync –no-sign-request
s3://openneuro/ds000030/ds000030_R1.0.5/uncompressed/{}/anat
./data/ds000030/{}/anat
download resting state fMRI scans
cat download_list |
xargs -I ‘{}’ aws s3 sync –no-sign-request
s3://openneuro/ds000030/ds000030_R1.0.5/uncompressed/{}/func
./data/ds000030/{}/func
–exclude ’*’
–include ‘task-rest_bold’
download fmriprep preprocessed anat data
cat download_list |
xargs -I ‘{}’ aws s3 sync –no-sign-request
s3://openneuro/ds000030/ds000030_R1.0.5/uncompressed/derivatives/fmriprep/{}/anat
./data/ds000030/derivatives/fmriprep/{}/anat
download fmriprep preprocessed func data
cat download_list |
xargs -I ‘{}’ aws s3 sync –no-sign-request
s3://openneuro/ds000030/ds000030_R1.0.5/uncompressed/derivatives/fmriprep/{}/func
./data/ds000030/derivatives/fmriprep/{}/func
–exclude ’*’
–include ‘task-rest_bold’
Finally open up the jupyter notebook to explore the tutorials:
cd sdc-bids-fmri
#Include below line if using anaconda environment source activate $(pwd)/sdc-fmri
jupyter notebook ```
Reference
[1] Gorgolewski KJ, Durnez J and Poldrack RA. Preprocessed Consortium for Neuropsychiatric Phenomics dataset [version 2; referees: 2 approved]. F1000Research 2017, 6:1262 (https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.11964.2)